Blogs
Who Provides Internet Service to Internet Service Providers – ISPs
Who Provides Internet Service to Internet Service Providers – ISPs
You need to understand what an Internet Service Provider is before understanding who offers an internet service to ISPs or internet service providers.
Definition of Internet service provider:
An ISP (Internet service provider) is an organization that offers services for using and accessing the Internet. The structure of internet service providers can take many different forms, including commercial, community-owned, non-profit, or other types of privately owned businesses.
An ISP community is the only industry which helps us in utilizing the benefits of internet and the great opportunities it holds for us. It only requires a modem and router for getting started.
The services provided by the ISP can include,
- Internet transit
- Internet access
- Domain name registration
- Collocation
- Usenet service
Now the question is who provides the internet to the ISPs?
ISPs provides data connection to their subscribers by virtue of which they can connect smartphones and other gadgets by using Wi-Fi routers available for providing internet. Also, they establish a high bandwidth connection(s) to either an internet exchange, or other ISPs, or as a combination of both. ISPs can also connect directly to (content) service providers or even host their servers directly inside one of their facilities (common with Google, Facebook, Netflix, etc.)
Let’s discuss some common terms used.
Peering
Peering is a method that allows two networks to connect and exchange traffic directly without having to pay a third party to carry traffic across the Internet.
In order to acquire the most traffic, two different types of tier networks are typically used, along with peering and bridging. The majority of large businesses choose to set up their own peering connections.
This approach is used by reputable internet service providers. They offered the subscribers access to their own network at the time of ISP peering. The entire processing is free, and neither ISP is paid by the other.
There are two types of Peering, one is public peering and another is private peering.
Peering at Internet Exchange Point (IXP) –
What is Internet Exchange Point (IXP)
Internet Exchange Point is a position where many ISPs interconnect their network together. Probably several peering sessions can be established across a single IXP peering.
IP-Transit
Small data providers prefer for IP-transit to operate.
This is typically utilized in situations where the ISP is unable to connect to the outside world.
As a result, IP-transit reaches people that ISPs cannot. In general, it involves transporting internet traffic that exists between continents.
Thus, it can be connected to different types of ISP that is a paid service. The payment of the ISP depends on the amount of traffic attracted by the IP-Transit.
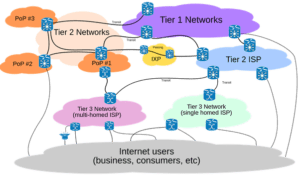
Network Tiers available in the market
1. Tier 1
It is the huge network intended for offering the internet to ISPs. Therefore, it is a kind of transit free network that is required for peering with every other tier 1.
2. Tier 2
This kind is required for peering with different type of networks, but still goes for payment settlement in order to reach some segment of the internet.
3. Tier 3
Tier 3 is a type of network, which purchases the transit from different types of networks in order to reach the internet.
These tiers are available depending on the cost and quality. All the three kinds of tiers are known as the high performance networks.
The major goal of employing these levels is to direct customers toward the preferred providers. The easiest strategy to reduce costs while maintaining the top tier is in this way. These layers are important because they protect customer choice.
Consequently, the networks are perfect for allowing the users to provide the widest types of internet service provider.
Subscribe to Newsletter
