An Internet service provider (ISP) is a company that provides customers with Internet access. Data is transferred using several technologies, dial-up, DSL, cable modem, wireless or high-speed interconnectors. Starting an ISP business is not as easy as it sounds. But with a proper plan and resources, it is not impossible either.
The biggest challenge to becoming an ISP in India is the huge amount of initial capital required for the licensing, equipment and infrastructure. Internet Network bandwidth, equipment cooling and power sources are all resources that have to be planned and executed properly.
Following are the steps to start an ISP:
- First step is to acquire an ISP (Internet Service Provider) License to run the business of Broadband in India. Any MSO can apply to obtain the ISP License UL (Unified Licensing) System. UL License is given by DoT and it is valid for 20 Years.
- One must decide the coverage of the area of the services offered. One can choose from three categories that is-
- Category A ISP: Covers the entire country.
- Category B ISP: Covers one of the 20 major states in India.
- Category C ISP: Covers one secondary switching area i.e. a small town, a village, a colony or a district.
- The third utmost important step is to have a NOC (Network Operations Centre) with raised floors that can route cables easily.
- The company will have to purchase, install and configure enterprise-grade routers, switches and computers. In addition, the company has to also purchase power backup solutions, in case of power cuts.
- The next step is to have bandwidth with minimum two or more upstream internet service from telecom providers like Reliance Com to resell it to the clients.
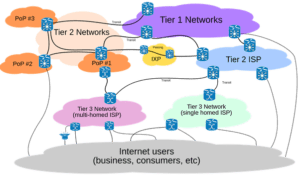
- A company can peer at an Internet Exchange and offload traffic and perhaps saves huge amount of Internet Bandwidth.
Eligibility Criteria for Internet Service Providers.
A company registered in India under the Companies Act, 1956 will be eligible to submit the proposal for providing Internet Service. Foreign equity shall be as per the Government policy and guidelines issued from time to time. At present, the foreign equity is permitted to the extent of 49 percent. There is no requirement for the applicant-company to have any prior experience in information technology or telecommunication services.
LICENSE FEE: The license fee shall be waived for a period of five years up-to 31.3.2003.The license fee to be paid relating to the period starting from 1.4.2003 by the Licensee company will be intimated on or before 1.4.2001 and shall be payable to the Telecom Authority irrespective of the time of entry of an ISP.
PERIOD OF VALIDITY OF THE LICENSE AND ITS EXTENSION: The license shall be valid for an initial period of ten years unless otherwise terminated. If requested by the Licensee, the extension may be granted by the Telecom Authority on suitable terms and conditions for a period of five years or more at a time.
TARIFF: ISP’s will be free to fix their own tariff. The tariff will be left open to be decided by market forces. However, the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) may review and fix a tariff at any time during the validity of the license which shall be binding on the Licensee.
NUMBER OF LICENSES FOR ISP’s: Applicants will be required to submit the separate application for each Service Area. An applicant company may be granted any number of licenses. There will also be no limit on the number of licenses that can be granted in a particular Service Area. The leased-line subscribers of the Service will be from within the Service Area but the dial-up-access subscribers could be located anywhere in the country.
OBSCENE MATERIAL AND CYBER LAWS: Flow of obscene, objectionable, unauthorized or any other content infringing copyrights, intellectual property right and against international and domestic Cyber laws (as and when established) in any form over the ISP’s network is not permitted.
COST OF APPLICATION FORM AND PROCESSING FEE: A nominal cost of Rs.1000/- for the Application Form and Rs.5000/- towards processing fee for each application which is non-refundable have been prescribed.
Steps to get ISP License in India:
About DE-CIX India:
DE-CIX India is an interconnection hub for the major Indian and international networks and is powered by DE-CIX which operates the world’s largest Internet Exchange. DE-CIX India runs carrier and datacenter- neutral Internet Exchange Points in the Indian cities Mumbai, Delhi, Chennai, and Kolkata.
- Mumbai: Web Werks DC2- Rabale
Netmgaic DC5- Chandivali
ST Telemedia DC- Prabhadevi
GPX Mumbai- Andheri
You can also apply for ASN directly by going to APNIC and IRINN websites.
Apply Now :